-
1 circuit design
English-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > circuit design
-
2 circuit design
<el> ■ Schaltungsentwurf m ; Chipdesign n ; Schaltkreisentwurf m<el> (gen.; e.g. chip design) ■ Schaltungsentwurf m -
3 computer-aided circuit design
computer-aided circuit design CACD, rechnergestützter Schaltungsentwurf m, rechnergestützte Schaltungsentwicklung f (für integrierte Schaltungen)English-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > computer-aided circuit design
-
4 customized circuit design
customized circuit design kundenspezifischer Schaltungsentwurf mEnglish-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > customized circuit design
-
5 transistor circuit design
transistor circuit design Transistorschaltungsentwurf mEnglish-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > transistor circuit design
-
6 transistor circuit design
<el> ■ Transistorschaltungsentwurf mEnglish-german technical dictionary > transistor circuit design
-
7 circuit level design
circuit level design Entwurf m auf SchaltbildebeneEnglish-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > circuit level design
-
8 chip design
<el> ■ Schaltungsentwurf m ; Chipdesign n -
9 custom-design circuit
custom-design circuit kundenspezifischer Schaltkreis mEnglish-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > custom-design circuit
-
10 custom integrated circuit
custom integrated circuit ( custom-design integrated circuit) kundenspezifischer integrierter Schaltkreis m, Kunden-IC mEnglish-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > custom integrated circuit
-
11 surface mount[ed] design
(SMD) <el> (circuit board production) ■ SMD nEnglish-german technical dictionary > surface mount[ed] design
-
12 chip layout
-
13 CACD
English-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > CACD
-
14 route
-
15 расчетный ток (электрической цепи)
- vorgesehener Betriebsstrom (eines Stromkreises), m
расчетный ток (электрической цепи)
Электрический ток, предназначенный для протекания в электрической цепи при нормальных условиях эксплуатации
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Расчетный ток определяют с учетом разновременности включения потребителей. Когда условия являются изменчивыми, расчетный ток представляет собой непрерывный ток, который привел бы компоненты цепи к той же самой температуре. Этот ток обозначают IB
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
design current (of an electric circuit)
electric current intended to be carried by an electric circuit in normal operation
[IEV number 826-11-10]FR
courant d'emploi (d'un circuit électrique), m
courant électrique destiné à être transporté dans un circuit électrique en fonctionnement normal
[IEV number 826-11-10]Тематики
EN
DE
- vorgesehener Betriebsstrom (eines Stromkreises), m
FR
- courant d'emploi (d'un circuit électrique), m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > расчетный ток (электрической цепи)
-
16 распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > распределительное устройство
-
по назначению:
-
17 НКУ распределения и управления
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > НКУ распределения и управления
-
18 print
1. nounclear/large print — deutlicher/großer Druck
editions in large print — Großdruckbücher; see also academic.ru/68194/small_print">small print
3) (published or printed state)be in/out of print — [Buch:] erhältlich/vergriffen sein
5) (Photog.) Abzug, der; (Cinemat.) Kopie, die6) (Textiles) (cloth with design) bedruckter Stoff2. transitive verb1) drucken [Buch, Zeitschrift, Geldschein usw.]2) (write) in Druckschrift schreiben3) (cause to be published) veröffentlichen [Artikel, Roman, Ansichten usw.]4) (Photog.) abziehen; (Cinemat.) kopieren5) (Textiles) bedrucken [Stoff]Phrasal Verbs:* * *[print] 1. noun1) (a mark made by pressure: a footprint; a fingerprint.) der Abdruck2) (printed lettering: I can't read the print in this book.) der Druck3) (a photograph made from a negative: I entered three prints for the photographic competition.) der Abzug4) (a printed reproduction of a painting or drawing.) der Druck2. verb1) (to mark (letters etc) on paper (by using a printing press etc): The invitations will be printed on white paper.) drucken2) (to publish (a book, article etc) in printed form: His new novel will be printed next month.) drucken3) (to produce (a photographic image) on paper: He develops and prints his own photographs.) abziehen4) (to mark designs on (cloth etc): When the cloth has been woven, it is dyed and printed.) bedrucken5) (to write, using capital letters: Please print your name and address.) in Druckbuchstaben schreiben•- printer- printing
- printing-press
- print-out
- in / out of print* * *[prɪnt]I. nbold \print Fettdruck min large \print in Großschriftto write sth in \print etw in Druckschrift schreibento appear in \print veröffentlicht [o gedruckt] werdento be in/out of \print erhältlich/vergriffen seinto get into \print erscheinen, gedruckt werdento go out of \print nicht mehr gedruckt [o aufgelegt] werdento put sth into \print etw in Druck gebento rush sth into \print etw schnell veröffentlichen3. (printed media)▪ in \print in der Pressefloral \print Blumenmuster ntto leave \prints Fingerabdrücke hinterlassento take sb's \prints jds Fingerabdrücke nehmen\printmaker Grafiker(in) m(f)\print scandal Presseskandal m\print union Druckergewerkschaft fIII. vt▪ to \print sth1. TYPO etw druckento \print a magazine/newspaper eine Zeitschrift/Zeitung herausgebento be \printed in hardback in gebundener Ausgabe erscheinento \print a special issue eine Sonderausgabe herausbringento \print only lies nur Lügen druckento \print the truth about sb/sth die Wahrheit über jdn/etw veröffentlichen3. COMPUT etw ausdrucken5. (on fabric) etw bedrucken\printed by hand handbedrucktto \print a pattern on sth etw mit einem Muster bedrucken, ein Muster auf etw akk [auf]drucken6. (write by hand) etw in Druckschrift [o Druckbuchstaben] schreibenplease \print your name below your signature schreiben Sie bitte ihren Namen in Druckbuchstaben unter ihre UnterschriftIV. vithe book is \printing das Buch ist im Druck2. (make copy) druckento \print in black and white/colour in schwarzweiß/Farbe drucken3. (write in unjoined letters) in Druckschrift [o Druckbuchstaben] schreibento \print clearly/sloppily deutlich/unleserlich schreiben* * *[prɪnt]1. nhe'll never get into print — er wird nie etwas veröffentlichen
See:→ also small print2) (= picture) Druck m4) (= fabric) bedruckter Stoff; (= cotton print) Kattun m; (= dress) bedrucktes Kleid; (of cotton) Kattunkleid nt5) (= impression of foot, hand etc) Abdruck ma thumb/paw print — ein Daumen-/Pfotenabdruck m
2. vt2) (= publish) story, picture veröffentlichen3) (= write in block letters) in Druckschrift schreiben5)hoof marks printed in the sand — Hufabdrücke pl im Sand
3. vi1) (printer, printing machine) druckenready to print (book) — druckfertig; machine druckbereit
2) (= write in block letters) in Druckschrift schreiben* * *print [prınt]A v/t1. drucken (lassen), in Druck geben:print in italics kursiv drucken;print waste makulieren2. ein Buch etc verlegen, herausgeben3. (ab)drucken:printed circuit ELEK gedruckter Schaltkreis4. bedrucken:printed (wall)paper bedruckte Tapete(n pl);printed goods Druckstoffe5. in Druckschrift schreiben:printed characters Druckbuchstaben6. einen Stempel etc aufdrücken (on dat), drücken (on auf akk), einen Eindruck, eine Spur hinterlassen (on auf dat), ein Muster etc ab-, aufdrucken, drücken (in in akk)8. print outb) COMPUT ausdruckenB v/i1. drucken:b) Abdrucke machenc) Drucker(in) sein2. gedruckt werden, sich im Druck befinden:3. in Druckschrift schreiben4. a) sich drucken lassenb) FOTO sich abziehen lassen:print badly schlechte Abzüge liefernC s1. TYPO Druck m:a) im Druck (erschienen),b) vorrätig (Buch);out of print vergriffen3. Druckschrift f, -buchstaben pl4. Drucksache f, -schrift f, besonders US Zeitung f, Blatt n:daily prints bes US Tageszeitungen;the prints pl bes US die Presse;rush into print sich in die Öffentlichkeit flüchten;appear in print im Druck erscheinen5. Aufdruck m6. Druck m (Bild etc)7. Druck m:a) (Stahl-, Kupfer) Stich m, Radierung fb) Holzschnitt mc) Lithografie f8. Zeitungspapier n10. (Finger- etc) Abdruck m, Eindruck m, Spur f:prints of steps Fußspuren oder -(s)tapfen;print of a wheel Radspur;print of a fox Fuchsfährte f11. Druckmuster n12. bedruckter Kattun, Druckstoff m:print dress Kattunkleid n13. FOTO Abzug m, Kopie f14. Lichtpause f15. TECHa) Stempel m, Form f:print cutter Formenschneider mb) (Butter- etc) Form f, (-)Model mc) Gesenk n (zum Formen von Metall)* * *1. nounclear/large print — deutlicher/großer Druck
editions in large print — Großdruckbücher; see also small print
be in/out of print — [Buch:] erhältlich/vergriffen sein
4) (printed picture or design) Druck, der5) (Photog.) Abzug, der; (Cinemat.) Kopie, die6) (Textiles) (cloth with design) bedruckter Stoff2. transitive verb1) drucken [Buch, Zeitschrift, Geldschein usw.]2) (write) in Druckschrift schreiben3) (cause to be published) veröffentlichen [Artikel, Roman, Ansichten usw.]4) (Photog.) abziehen; (Cinemat.) kopieren5) (Textiles) bedrucken [Stoff]Phrasal Verbs:* * *n.Druck -e m.Fotoabzug m. v.drucken v. -
19 длительный допустимый ток
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
-
20 контактор (контактный)
контактор (механический) 1
Контактный коммутационный аппарат с единственным положением покоя, с управлением не вручную, способным включать, проводить и отключать токи в нормальных условиях цепи, в том числе при рабочих перегрузках.
МЭК 60050(441-14-33).
Примечание. Контакторы можно характеризовать способом, которым обеспечивается создание усилия для замыкания главных контактов
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
контактор
Двухпозиционный аппарат с самовозвратом, предназначенный для частых коммутаций токов, не превышающих токи перегрузки, и приводимый в действие двигательным приводом.
Примечание. Для аналогичных аппаратов без самовозврата следует применять термин «Контактор без самовозврата».
[ ГОСТ 17703-72]
контактор
Выключатель для дистанционного включения, отключения и переключения силовых электрических цепей
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
(mechanical) contactor
a mechanical switching device having only one position of rest, operated otherwise than by hand, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions including operating overload conditions
NOTE – Contactors may be designated according to the method by which the force for closing the main contacts is provided.
[IEV number 441-14-33]FR
contacteur (mécanique)
appareil mécanique de connexion ayant une seule position de repos, commandé autrement qu'à la main, capable d'établir, de supporter et d'interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, y compris les conditions de surcharge en service
NOTE – Les contacteurs peuvent être désignés suivant la façon dont est fourni l'effort nécessaire à la fermeture des contacts principaux.
[IEV number 441-14-33]1 Должно быть " контактный"
См., например, выключатель (контактный) - (mechanical) switch
Коммутационные аппараты следует классифицировать на контактные и полупроводниковые (solid-state)
[Интент]1. Контактор на относительно небольшой номинальный ток, это такой же коммутационный аппарат, как и пускатель, но без теплового реле (можно сказать, что пускатель это контактор плюс тепловое реле).
2. Контактор на большой номинальный ток выглядит совсем иначе
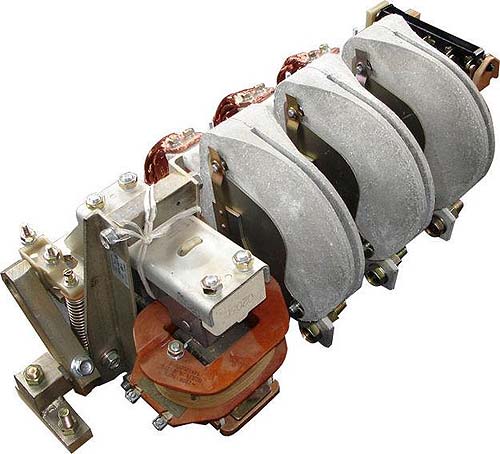
Отечественный контактор КТ-6063Число полюсов: 3
Номинальное напряжение главной цепи: 380 В
Номинальный ток главной цепи: 1000 А
Номинальное напряжение катушки: 380 В переменного тока
Контакторы электромагнитные серии КТ 6000 с естественным воздушным охлаждением предназначены для включения и отключения приемников электрической энергии на номинальное напряжение до 380 В переменного тока частоты 50 и 60Гц.
Используются в составе оборудования для включения мощных электрических машин и в аппаратуре автоматического включения резерва (АВР).3. Контакторами называют также коммутационные аппараты, коммутационная способность которых больше коммутационной способности реле (см. рис. ниже)
[Интент]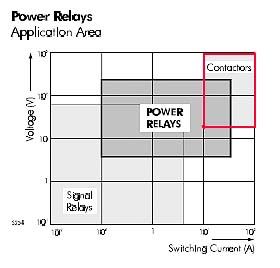
Рис. Tyco ElectronicsПараллельные тексты EN-RU
Although contactors are not strictly relays they have the same design principles. Like relays, they are remote controlled switches.
The difference is the considerably higher input power consumption, higher switching capacity, and larger size.
[Tyco Electronics]Хотя, строго говоря, контакторы не являются реле, их конструкция имеет много общего с конструкцией реле. Также как и реле, они представляют собой коммутационный аппарат с дистационным управлением.
Отличие состоит в том, что их входная цепь потребляет значительно больший ток, они имеют существенно большую коммутационную способность и их размеры также больше размеров реле.
[Перевод Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Действия
Неправильно:- замыкать контактор; - размыкать контакторСинонимы
EN
- contact-maker
- contactor
- electric contactor
- electromechanical contactor
- M/C
- magnetic contactor
- mechanical contactor
- power contactor
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > контактор (контактный)
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
Circuit design — The process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems all the way down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. For simple circuits the design process can often be done by one person without… … Wikipedia
circuit design — grandinių projektavimas statusas T sritis automatika atitikmenys: angl. circuit design; circuit engineering; circuit technique vok. Schaltungsentwurf, m; Schaltungstechnik, f rus. проектирование схем, n; схемотехника, f pranc. circuiterie, f;… … Automatikos terminų žodynas
Circuit design language — is a circuit schematic has been extracted to a CDL netlist for simulation. Several vendors such as Cadence, Calibre, and Synopsys support CDL netlists. Categories: Electronic circuitsElectronics stubs … Wikipedia
Integrated circuit design — Layout view of a simple CMOS Operational Amplifier ( inputs are to the left and the compensation capacitor is to the right ). The metal layers are colored blue and green, the polysilicon is red and vias are crosses. Integrated circuit design, or… … Wikipedia
Electronic circuit design — Methods To design any electrical circuit, either analog or digital, electrical engineers need to be able to predict the voltages and currents at all places within the circuit. Linear circuits, that is, circuits with the same input and output… … Wikipedia
integrated circuit design — integrinių grandynų projektavimas statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. integrated circuit design; integrated circuit engineering; microcircuit engineering vok. Entwurf integrierter Schaltkreise, m; Mikroschaltungstechnik, f;… … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
bipolar integrated circuit design — dvipolių integrinių grandynų sukūrimas statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. bipolar integrated circuit design vok. Bipolar Design, n; Entwurf von bipolaren Schaltungen, m rus. разработка биполярных интегральных схем, f pranc.… … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
integrated-circuit design language — integrinių grandynų kompiuterinio projektavimo kalba statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. integrated circuit design language vok. Entwurfssprache für integrierte Schaltkreise, f rus. язык автоматизированного проектирования… … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
hybrid circuit design — hibridinių grandynų projektavimas statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. hybrid circuit design vok. Hybridschaltungsentwurf, m rus. проектирование гибридных схем, n pranc. conception des circuits hybrides, f … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
custom integrated circuit design — užsakomųjų integrinių grandynų projektavimas statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. custom integrated circuit design vok. Kundenwunsch Schaltkreisentwurf, m rus. проектирование заказных интегральных схем, n; разработка заказных… … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
Design for testing — Design for Test (aka Design for Testability or DFT ) is a name for design techniques that add certain testability features to a microelectronic hardware product design. The premise of the added features is that they make it easier to develop and… … Wikipedia
